Published On Apr 16, 2019
#Satellite #AnimatedChemistry #KineticSchool
Chapters:
0:00 Kinetic school's intro
0:18 Satellite
0:32 Types of satellite orbits By Inclination
1:15 Launching an artificial satellite
2:39 How satellite works
3:43 Types of satellite orbits by inclination
6:08 Types of satellite orbits by Altitude
8:13 Types of satellite orbits by Shape
9:46 Types of Artificial satellite
More videos:
What is Greenhouse Effect? Explained.
• Greenhouse Gases and Greenhouse Effec...
Layers of the Atmosphere
• Layers of the Atmosphere (Animation)
How Lightning Forms
• How Lightning Forms (Animation)
Photochemical Smog
• Photochemical Smog (Animation)
Acid Rain
• Acid Rain (Animation)
Sources of Air Pollution
• Sources of Air Pollution (Animation)
Air Pollution
• Air Pollution (Animation)
How Battery Works
• How Battery Works (Animation)
SATELLITE:
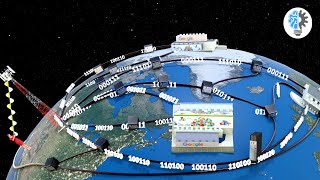
A satellite is any object that revolves in a curved path around a planet.
There are two major types of categorization when it comes down to satellites, one is natural Satellite and the other is artificial satellite.
A Natural Satellite is any celestial body in space that orbits around a larger body.
Satellites that are made by people and launched into orbit using rockets are called Artificial Satellites.
TYPES OF satellite orbits:
By Inclination,
Equatorial orbit:
An equatorial orbit is when the satellite rotates in an orbit directly above the equator,
usually in a circular path. with an equatorial orbit, the angle of inclination is 00 degrees.
It has an inclination of 0°.
Inclined orbit:
Inclined orbits are virtually all orbits except those that travel directly above the equator or directly above the North and South Poles. The angle of inclination vary between 0 to 180 degrees.
Polar orbit:
A polar orbit is when the satellite rotates in a path that takes it over the North and South Poles in an orbital pattern that is perpendicular to the equatorial plane.Polar orbiting satellites follow a low altitude path close to earth’s surface, passing over and very close to both the North and South Poles.
The angle of inclination of a satellite in a polar orbit is nearly 90 degrees.
On the basis of the altitude from Earth, the types of orbits are classified into:
• Low Earth orbit (LEO):
Low earth orbit satellites operate at a distance of about 160 to 2,000 kilometres above the earth's surface.
It takes approximately 90 to 120 minutes to circle the Earth.
• Medium earth orbit (MEO):
Medium earth orbit is the region of space around the Earth above low Earth orbit and below geostationary orbit.
The orbital periods of Medium earth orbit satellites range from about two to six hours.
This satellite operates at altitudes between 2,000 kilometers and 35,786 kilometers above the earth’s surface.
• Geostationary earth orbit (GEO):
A geostationary satellite is an earth-orbiting satellite. it placed at an altitude of approximately 35,786 kilometers directly over the equator, that revolves in the same direction the earth rotates that means west to east.
This satellite takes 24 hours to orbit the Earth.
Orbits are also classified into two types on the basis of the shape:
• Circular orbit
• Elliptical orbit
Circular orbit:
Circular orbit is the orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter, that is, in the shape of a circle. This orbits has an eccentricity of 0.
There are several types of circular orbits and they include:
• Geostationary Orbit
• Polar Orbit
• Equatorial orbit
Elliptical Orbit:
An elliptical orbit is the revolving of one object around another in an oval-shaped path called an ellipse.
The eccentricity of an elliptical orbit is greater than 0 but less than 1.
Sometimes these satellites are closer, and at other times they are farther away from earth.
The closest point a satellite comes to Earth is called its perigee.
The farthest point is the apogee.
The most common example of elliptical orbit is highly elliptical orbit.
Types of artificial satellites
Navigation satellite:
A satellite navigation system used to determine the ground position of an object.
It determines the geographic location of ships, aircrafts, or any other object.
It is also vital to military forces.
It is often used for gathering intelligence used for military purposes or as a military weapon.
Weather satellite:
Weather satellites are primarily used-
✓ to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth.
✓ to predict daily weather conditions, such as temperature and rainfall.
✓ to monitor how weather conditions, like storms, hurricanes, cyclone, tropical storms,
develop and change over time.
Communications satellite
The communication satellite is a satellite that transmits the signals such as telephone, television, radio, internet signals over long distances.